Usability testing is a research that is conducted to study the usability of a web page, user interface or device for its further mass use. In other words, the main goal of usability testing is a preliminary check of the product to see if it is easy, simple and convenient to use for the average user.
Here is a simple example of why usability testing is so important for your product. Just imagine: you are preparing dinner for your guests who are going to come soon. There is a wonderful dish set on the table, there is a bottle of dry red wine near at hand. Your pasta is almost ready. What is better now: to taste the pasta before the guests come, or to blush (like that red wine) and take the oversalted pasta off the table in the presence of the guests? The answer seems to be obvious!
The need for usability testing
What is the purpose of a usability test? Aesthetics, comfort and design are incredibly important. The program can be as useful as possible, but if the "wrapper" is ten years behind the modern style, the application is unlikely to grab many users. On the other hand, the design can be great, but if the program is difficult to use, many people will immediately abandon it. In a technical sense, usability testing is a test of an application for user experience.
There are a number of user issues that need to be solved before a product can be launched:
- Where should I click next?
- Which page do I need to go to next?
- What does this icon mean?
- Where should I find the menu?
- Why isn’t the error message displayed effectively?
- Why is one session not enough to address the need?

If you solve these and other issues before launching the product, it can be saved from market failure. Furthermore, usability testing can help to come up with ideas on how to solve the problems on which the team usually spends too much time. Thus, there are many benefits in usability testing.
Usability testing methods
There are two usability testing methods for websites, applications and other interfaces - qualitative and quantitative.
Qualitative testing is the collection of information, problems and conclusions about the ways the client uses a particular service. This is a common form of usability testing.
Quantitative testing is the testing of a product for user experience. The main metrics are a success, achievement of the goal by a user and the time spent on the task.
It is usually recommended to involve five people in the test to detect any system errors.
Usability testing can also be divided into remote and personal. Remote testing is more popular because it does not require much money and time.
How to conduct a usability test? Usability testing is a kind of "game" with two actors: the facilitator and the participant. Both have to complete certain tasks. The facilitator forms the task and passes/forwards it to the participant. The latter performs the task and pays attention to the drawbacks of the system. At this time the facilitator monitors the participant's behaviour and receives feedback from him or her.
What should be done during usability testing?
The main character of this game is a facilitator. This is a person who forms the task and monitors the behaviour of the participant. Subsequently, when analyzing the records of the session, he/she makes a list of drawbacks as well as wishes of all participants.
Based on these data, the team improves the program. Being on the outside looking in, this process may seem too easy and too simple, but in reality, it takes time, needs a successful setting of the task and effective implementation of the conclusions into the program.
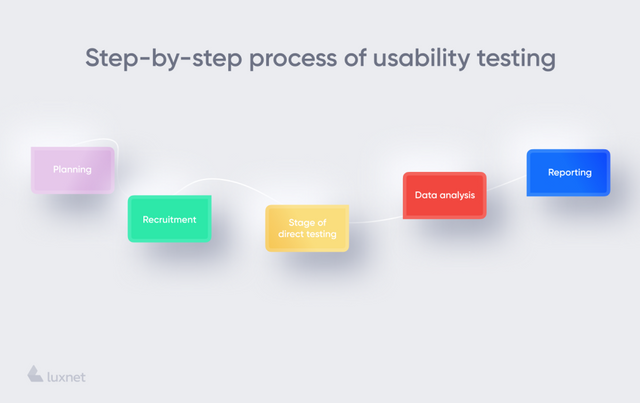
Step-by-step process of usability testing:
Planning. Set goals for which you use usability testing. Identify the critical functions of the system, formulate the task correctly. Make it narrow. "Sit down and look at the app. Do you like it?" This is not a very pleasant task. Focus the tester's attention on the important aspects: Is the user experience well executed? Is it possible to understand intuitively where the functions are? Is the design of the application pleasing to the eye?
Recruitment. Form your target audience (TA) and only after that look for the testers. Pay attention to demographic, professional and other indicators of your TA. It is unlikely that a sixteen-year-old boy will be able to identify drawbacks in the application which informs and allows you to experience trading and investing.
Stage of direct testing. At this stage, the participant uses the program.
Data analysis. The facilitator analyzes the information received from the participants.
Reporting. Test results are distributed to the entire team. This can be a developer, designer, client, etc.
Examples of testing
It can often seem that usability testing is unnecessary. Something like: your whole team has reviewed the previous layouts, you have studied all the details once again, and actually, you are ready to run the application… But in a few days, your rating drops from five to two and a half in an online store. Everything is due to the details that are invisible to you: not quite a user-friendly interface, very loud notifications, or design that strains the eyes.
Usability testing will be definitely needed here: it provides the possibility to detect the system bugs before, but not after the start. In theory, this will save money in your business: after all, testing is undoubtedly cheaper than lost reputation and development of a new system.
For example, the worldwide booking site Airbnb has also ordered usability testing before launching new functions. The testers were asked to book a room or tour, cancel a reservation, contact for support, and ask the homeowner how to get to their house. These are just good examples of successful tasks: they are narrow, important and play a significant role when used by a large number of people.
The application was also tested by the Uber transportation company: the testers were asked to cancel the trip, add the method of payment, complain about the driver, and so on. And after receiving the results, they always changed the system to make it more convenient.
Conclusions
That's why we believe that usability testing has many benefits:
- open feedback from the audience and the possibility to improve the program;
- problems and potential drawbacks can be identified before launching the program;
- minimizing the risks that the product will fail;
- in the future, there is a high probability that the user will come back & use a quality product again.
Usability testing is a story about two components that complement each other:
users achieve their goals better and faster = business achieves its goals better and faster.
