User experience research is about knowing everything about your customer, identifying his/her pain points and processes of satisfaction. Everything is in order to take the product to a new level, where the user can find your service and think: “This is all I wanted! This is all as I wanted!” UX research will help turn a potential customer into a regular one. Where to start and how to do it, we’ll tell in this article.
What is UX research as a process?
Your audience is live people. Each of them has their own unique needs, desires, emotions and style of shopping or ordering services. The user goes to the site or application to purchase a specific product and all he/she needs for this is a comfortable UX design. If the platform is user-friendly and you don't have to think hard about the necessary buttons/pages while visiting the website, the purchase will be successful.
Well, how are you going to find out what's right for your target audience and what's not? Qualitative and quantitative research in UX design is rushing to the rescue. Analyze your users' mental models: find out about their deep-rooted concepts, generalizations, and even pictures and images that affect the way they perceive the world. Implement user experience study in the company - the customer’s intuition when visiting the site. Understand your user.
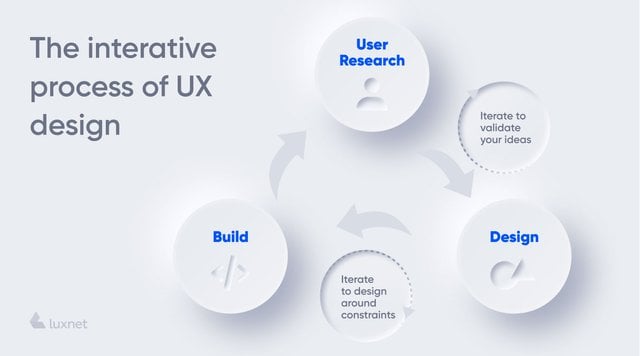
The main principles
Let’s imagine that all of a sudden you decide to start training in the gym. Your days (and sedentary lifestyle, by the way) need sport! But this idea comes to your mind at half-past two at night. What should you do? Apparently, if you haven't fallen asleep yet, you'll start ... looking for information on the Internet. And how exactly? How do you choose the needed site?
Before you read on, give yourself the answers to these questions.

Will you go to the maps and look for the gym that is the closest to your location? Will you enter the word "gym" and the name of your city in the search engine? Or will you search for tags on social networks or write messages to your friends who are athletes? What action will you choose?
The answers to these and hundreds of other questions are provided by user experience research. Yes, when doing it, you need to come to people and talk to them (unexpectedly); sometimes you have to keep an eye on them (it can be a little bit scary). However, without high-quality sociology, it is impossible to create a site the user will definitely visit.
In a technical sense, the main task of user experience research is to identify and form well-defined types of users, learn about them as much as possible, and also to determine the strengths and weaknesses of your business.
There are two main types of user research:
1. Quantitative user research. It's about statistics. You can calculate and figure out a certain number of users, preferences, visits, etc. This type pays attention to numbers and mathematics.
2. Qualitative UX research methods. Understanding is important here. First of all, qualitative type concerns representations and descriptions. In other words, those things that cannot be calculated but can be seen and understood.

These types of user testing should be divided into three stages:
1. Strategy. At this stage, it is necessary to consider the current state of things and think about new ideas and opportunities for the future. What needs to be improved? What is necessary to remove and what, on the contrary, to add? What should your product or service look like?
2. Implementation. If you already have clear answers to the questions above, you can proceed to the next stage. Here you are to form the focus groups and study the audience. At this stage, you can use the following methods:
- Card sorting: allows users to gather information about a website into a logical structure that administers the navigation and information architecture of the site. This is a kind of guarantee that the structure of the site will meet the expectations and skills of users.
- Field study: this is the most interesting part. You need to go to the "fields", talk to users, find out their opinions. You can do this through social networks, questionnaires, feedback. If you are brave enough, you can talk to users offline:)
- Usability testing: you should research to study the convenience of a web page, user interface or device for its further mass use. To do this, create a focus group of ordinary people, i.e. potential users.
3. Evaluation: This is the moment when the service is available to a large number of users. At this stage, you can assess how good and qualitative the product is, as well as the service around this product. This is a kind of outcome evaluated on the basis of historical product data or opposition to competitors.
So why do I need it?
UX research is very useful for developing product strategies and making algorithm solutions that would meet user needs. Nowadays the companies are thinking more and more about improving the user experience because it is really helpful. In this way, the business learns what attracts the user, what he/she likes and what dislikes. The most important aspect here is how the customer finds a product or service and why he/she returns. The whole team is involved in this process: developers think about how to improve UX design, content makers deal with the content improving, designers are engaged in a high-quality and user-friendly user interface, and so on.
Goals and results of user experience research
The purpose of UX research is to establish the connection between the product and the context you mean. Let’s take the same gym, for example. This time, imagine you are its owner. What is your goal? Is it to create a place where everyone can feel free? Or maybe to make the best gym in the city where the equipment does not lag behind the world sports trends? Is it to teach people to love their bodies or teach them endurance? What does the product you present to users look like? In addition, in what context do you do it? Obviously, the information about you on the site and other social platforms must be true; but there's one more thing here: all these interactive data have to match what you're offering to your target audience. Conventionally speaking, UX research ensures that you create a project based on the user needs and, at the same time, you do not impose information on him/her. It's as if a customer comes to your site and thinks, "Oh, that's exactly what I was looking for!" In fact,
he/she doesn't reread the long issues in the "blogs" section, agree or disagree with you. The customer just thinks you have guessed all his/her needs, pains, fears.
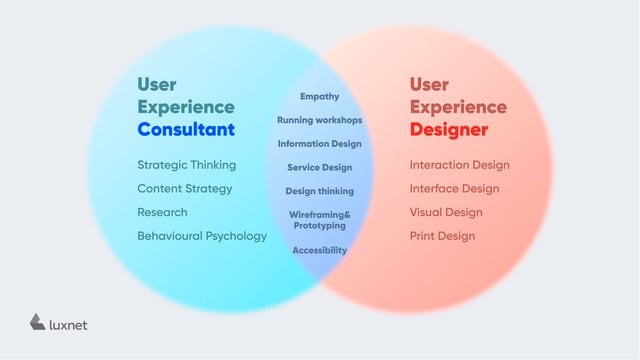
Differences between UX designers and UX researchers
Finally, so as not to confuse you: primarily, two people are working to create a quality and user-friendly user experience - a designer and a researcher.
The UX researcher takes the first step. He/she analyzes the market and forms the target audience. The researcher answers the questions: Who is the user of the product? What motivates him/her to use this or that service? How is it convenient for him/her to do it? The basis for creating a quality service is strategy and understanding.
The task of the UX designer is to develop a convenient and intuitively clear design based on the received data. This is the design of user experience (experience design) that will help the customer to choose the desired service. Literally, the designer simplifies the buying process: he/she makes it pleasant and easy.
Conclusions
Your project can be compared to a house. For sure, it is difficult to build a house without a foundation. When creating or improving service, clear and structured knowledge about the product and the target audience is the necessary foundation. You can invest a lot of money in the project and hire the best employees from different industries, but without quality analytics, the business will not satisfy either you or the user.